Numerical Simulation of Architectural Environment
Platform of Inter-/Transdisciplinary Energy Research, Faculty of Engineering
Department of Architecture, Graduate School of Human-Environment Studies
Department of Architecture, School of Engineering
Buildings account for 30% of the total CO2 emissions in Japan, and to achieve carbon neutrality, it is essential to make buildings more energy efficient. On the other hand, due to the effects of the recent coronavirus pandemic, well-being has been attracting even more attention, and architectural environmental design that balances energy conservation and well-being has become important. In order to create an indoor environment that is healthy, comfortable, and productive, it is important to comprehensively predict and evaluate the interaction between indoor environmental elements and the human body, but in the case of experiment-based research, due to time, space, cost, and ethical constraints, numerical experiments (simulations) based on digital twins of the built environment have attracted attention as a new approach to research in recent years.
This laboratory is engaged in research on the development and utilization of numerical analysis models that enable comprehensive evaluation of the quality of the indoor environment, represented by the thermal environment and air quality, as well as human health and comfort.
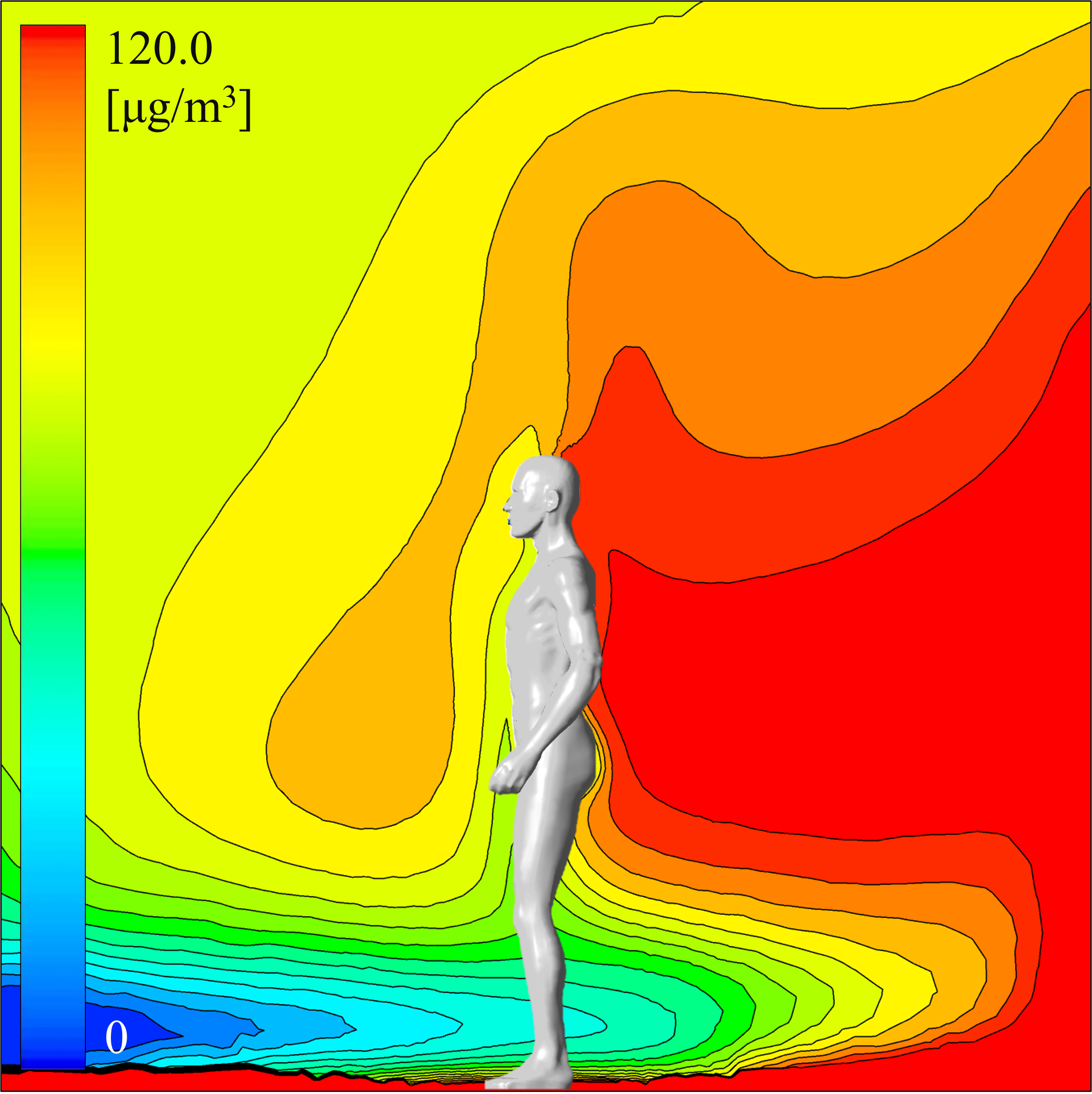
Indoor environment simulation using numerical human body model
Staff
Assoc.Prof. Sung-Jun Yoo
The Main Research Topics
- Comprehensive evaluation of indoor air quality and thermal comfort using a numerical human body model
- Research on indoor environment design and optimization of HVAC control
- Research on the advancement of numerical human body models
- Research on optimal design of air conditioning and ventilation equipment













