Hydrogen Production Processes
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering
Department of Hydrogen Energy Systems, Graduate School of Engineering
Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Engineering
To achieve carbon neutrality, the effective use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal power is becoming increasingly important. To utilize these energy sources efficiently, energy storage technologies are essential.
Water electrolysis is a key method for producing hydrogen using electricity derived from renewable sources. It converts electrical energy into storable hydrogen.
Proton-conducting oxides are ceramic materials capable of conducting hydrogen ions. When used to electrolyze steam, these materials enable hydrogen production with over 30% less electricity compared to conventional water electrolysis. Moreover, if part of the required energy can be supplied as heat, electricity consumption can be further reduced. It is also crucial to develop reliable equipment at low cost.
Our research focuses on hydrogen production based on electrochemical principles, with an emphasis on producing hydrogen efficiently and economically.
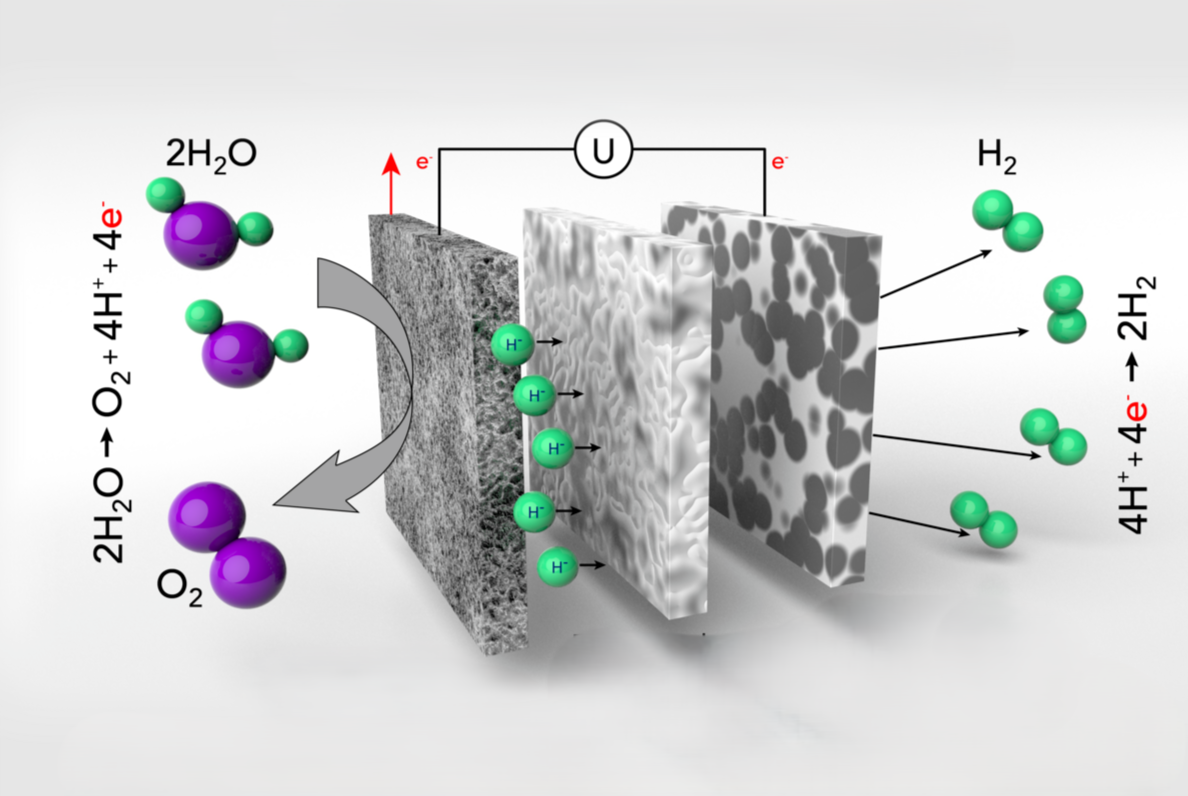
Hydrogen production via steam electrolysis using proton-conducting oxide electrolyte
Staff
Prof. Hiroshige Matsumoto
Assoc.Prof. Leonard Kwati
The Main Research Topics
- Steam Electrolysis Using Proton-Conducting Oxides
- Fabrication and Processing of Metal Oxide Cells
- Integrated Use of Electricity and Heat for Hydrogen Production













